Urology is a specialized branch of medicine that focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of disorders affecting the male and female urinary tract systems, as well as the male reproductive system. Urologists are trained medical professionals who are experts in managing conditions that affect these crucial bodily systems.
Understanding the Urinary Tract
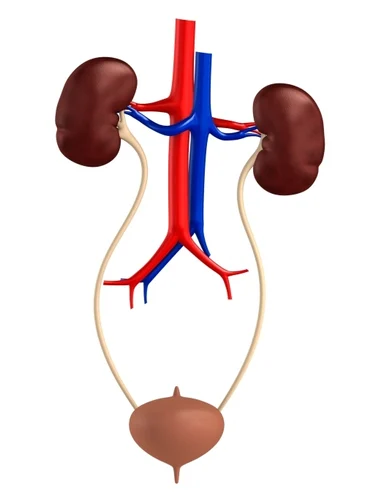
The urinary tract comprises various organs responsible for the production, storage, and elimination of urine. These include the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter waste products from the blood to produce urine, which then travels through the ureters to the bladder for storage. The bladder, in turn, expels urine through the urethra during urination.
Scope of Urology
Urologists diagnose and treat a wide range of conditions that can affect any part of the urinary tract and male reproductive system. Some common urological conditions include:
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Infections that can occur anywhere in the urinary tract, typically caused by bacteria.
- Kidney Stones: Hard deposits of minerals and salts that form within the kidneys and can cause severe pain and complications.
- Prostate Conditions: Such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostate cancer, which affect the prostate gland in men.
- Erectile Dysfunction: The inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse.
- Incontinence: The involuntary leakage of urine, which can be caused by various factors including weakened pelvic floor muscles or nerve damage.
- Male Infertility: Issues affecting sperm production or transport that may lead to difficulties in conception.
- Cancers: Urologists also diagnose and treat cancers of the kidneys, bladder, prostate, and testicles.
Diagnostic Techniques and Treatments
Urologists employ a variety of diagnostic techniques to assess and diagnose urological conditions. These may include physical examinations, urine tests, blood tests, imaging studies (such as ultrasound or CT scans), and specialized procedures like cystoscopy (examining the bladder with a thin camera).
Treatment options vary depending on the specific condition but can include medications, lifestyle modifications, minimally invasive procedures (like laser surgery for kidney stones), and major surgeries for complex conditions.
Collaboration with Other Specialties
Due to the interconnected nature of urological conditions with other bodily systems, urologists often collaborate with specialists in oncology, nephrology, gynecology, and reproductive medicine to provide comprehensive care to patients.
Importance of Urological Health
Maintaining urological health is crucial for overall well-being and quality of life. Regular check-ups with a urologist can help in early detection and treatment of potential issues, thereby preventing complications and ensuring optimal health outcomes.
In conclusion, urology plays a vital role in managing and treating conditions affecting the urinary tract and male reproductive system. Through advanced diagnostic techniques and a range of treatment options, urologists help patients manage urological conditions effectively, improving their quality of life and overall health.





Comments