When it comes to diagnosing various health conditions, particularly cancers and other serious diseases, a biopsy is a crucial tool. This medical procedure involves the removal of a small sample of tissue from the body to be examined under a microscope. A biopsy can provide definitive information about the presence, nature, and extent of a disease, which significantly influences the subsequent treatment plan. In this article, we'll explore the importance of biopsies in diagnosis and how they contribute to improved treatment outcomes.
Understanding the Biopsy Procedure
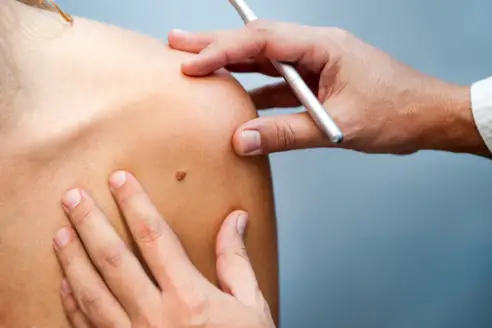
Biopsy for Diagnosis Purposes in Dubai involves extracting tissue from a specific area of the body where there is a suspected problem. This sample is then analyzed in a laboratory to determine the presence of disease and its characteristics. There are several types of biopsy procedures, including:
- Needle Biopsy: A thin needle is used to remove a small amount of tissue. This can be done with a fine needle for fluid or cells, or a core needle for a larger tissue sample.
- Endoscopic Biopsy: An endoscope (a flexible tube with a camera and tools) is inserted through a natural body opening or a small incision to obtain tissue samples.
- Surgical Biopsy: In cases where other biopsy methods are not feasible, a small surgical procedure may be performed to remove a part or the entire affected area.
The Role of Biopsy in Diagnosis
The key role of a biopsy is to provide a definitive diagnosis. This process allows healthcare providers to:
- Identify Disease Presence: Biopsies are essential in confirming whether a particular disease, such as cancer, is present. While imaging tests can indicate abnormalities, only a biopsy can definitively confirm a diagnosis.
- Determine Disease Type and Grade: For cancers and other tumors, a biopsy helps in determining the type of cancer and its grade (how aggressive or advanced the cancer is). This information is crucial for planning the most effective treatment.
- Assess Disease Spread: In some cases, biopsies can provide insights into whether and how far a disease has spread, which is vital for staging the disease and planning treatment.
Types of Biopsies and Their Uses
Different biopsy techniques are used based on the location of the suspected disease and the type of tissue involved. Some common biopsy types include:
- Skin Biopsy: Used for diagnosing skin conditions, including skin cancer. Methods include punch biopsy, shave biopsy, and excisional biopsy.
- Breast Biopsy: Performed when abnormalities are detected in breast tissue. Techniques include needle biopsy (fine needle aspiration or core needle biopsy) and surgical biopsy.
- Liver Biopsy: Helps diagnose liver diseases such as hepatitis or cirrhosis. It can be done percutaneously (through the skin) or via laparoscopy (a minimally invasive surgical procedure).
Preparing for a Biopsy
Preparation for a biopsy depends on the type of procedure being performed. Generally, patients may need to:
- Follow Specific Instructions: Depending on the biopsy type, you may need to fast or avoid certain medications. It's essential to follow the doctor's pre-procedure instructions carefully.
- Discuss Concerns: Address any concerns or questions with your healthcare provider. Understanding the procedure, risks, and expected outcomes can help alleviate anxiety.
The Biopsy Process and Recovery
The biopsy procedure itself is relatively straightforward, though the experience may vary based on the type of biopsy. Here’s what typically happens:
- Local Anesthesia: Most biopsy procedures are performed under local anesthesia to numb the area and minimize discomfort.
- Tissue Collection: The sample is collected using the appropriate technique (needle, endoscopic tool, or surgical method).
- Post-Procedure Care: After the biopsy, there might be minor discomfort, bruising, or swelling. Following care instructions and attending follow-up appointments are important for a smooth recovery.
The Importance of Biopsy Results
The results from a biopsy are crucial for determining the next steps in treatment. They help healthcare providers:
- Formulate a Treatment Plan: Based on the biopsy results, doctors can develop a targeted treatment plan tailored to the specific type and stage of the disease.
- Monitor Disease Progress: Biopsies can also be used to monitor how well a treatment is working by comparing pre- and post-treatment samples.
Potential Risks and Complications
While biopsies are generally safe, there are potential risks and complications, such as:
- Infection: As with any procedure that involves breaking the skin, there is a risk of infection.
- Bleeding: Some bleeding at the biopsy site is normal, but excessive bleeding is a potential risk.
- Pain: Mild to moderate pain or discomfort is common, but it usually subsides within a few days.
Conclusion
A biopsy is a powerful diagnostic tool that provides essential information for diagnosing and treating various medical conditions. By allowing for precise diagnosis, determining disease characteristics, and guiding treatment decisions, biopsies play a pivotal role in improving patient outcomes. If you’re advised to undergo a biopsy, understanding the procedure and its significance can help you feel more confident and informed about your healthcare journey.




Comments