Introduction
Warts, though common, can be bothersome and even embarrassing. How To Choose The Right Treatment For Warts? Fortunately, there are numerous treatment options available to help get rid of them. However, choosing the right wart treatment can be challenging, as there are various factors to consider. In this article, we'll explore the different types of warts, factors to consider when selecting a treatment, various treatment options, and how to make an informed decision.
Understanding Warts
Warts are non-cancerous growths caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). They can appear anywhere on the body and are typically skin-colored or slightly darker. Warts are contagious and can spread through direct contact.
Types of Warts
Common Warts
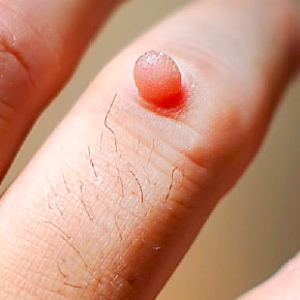
Common warts usually appear on the hands, fingers, or elbows. They have a rough texture and may have black dots (clotted blood vessels) on the surface.
Plantar Warts
Plantar warts develop on the soles of the feet and can be painful, especially when walking. They often have black dots and may grow inward due to pressure from walking or standing.
Flat Warts
Flat warts are smaller and smoother than other types of warts. They often appear in clusters on the face, arms, or legs and can be flesh-colored, pink, or light brown.
Filiform Warts
Filiform warts are long and narrow, usually appearing on the face, especially around the eyes, mouth, or nose. They have a thread-like appearance and can be flesh-colored or slightly darker.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Wart Treatment
Several factors should be taken into account when selecting a wart treatment:
- Location of the wart: Warts in sensitive areas may require a different treatment approach.
- Size of the wart: Larger warts may need more aggressive treatment methods.
- Pain tolerance: Some treatments may cause discomfort or pain.
- Cost of treatment: Different treatments have varying costs.
- Convenience and availability: Consider the time and effort required for each treatment option.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Wart Treatments
Salicylic Acid
Salicylic acid is a common ingredient in OTC wart treatments. It works by breaking down the skin cells of the wart, gradually causing it to peel away.
Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy involves freezing the wart with liquid nitrogen. This method destroys the wart tissue, causing it to fall off over time.
Duct Tape Occlusion
Duct tape occlusion involves covering the wart with duct tape for several days to suffocate it. This method may take several weeks to show results.
Prescription Wart Treatments
Cantharidin
Cantharidin is a chemical compound that is applied to the wart and causes blistering. The blister containing the wart is then removed after a few days.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy involves stimulating the body's immune system to fight the wart virus. This can be done through various methods, such as injecting antigens into the wart.
Surgical Removal
Surgical removal may be necessary for large or stubborn warts. This can be done through excision, laser surgery, or electrocautery.
Natural Remedies for Warts
Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar is a popular home remedy for warts. It is applied directly to the wart and may help break down the tissue.
Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil has antiviral properties and can be applied topically to warts. It may help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
Garlic
Garlic contains compounds that have antiviral properties. Crushed garlic cloves can be applied directly to warts or consumed orally.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
It's essential to consult a healthcare professional before starting any wart treatment, especially for persistent or recurrent warts. They can provide personalized recommendations based on the type and location of the wart, as well as your medical history.
Conclusion
Choosing the right wart treatment requires careful consideration of various factors, including the type and location of the wart, pain tolerance, cost, and convenience. Whether opting for OTC treatments, prescription medications, or natural remedies, consulting a healthcare professional is key to ensuring effective and safe treatment.




Comments