Introduction
In modern networking environments, Inter-VLAN routing configuration plays a crucial role in enabling seamless communication and enhancing network security. As businesses grow and networks expand, the need for isolated VLANs becomes inevitable to improve performance and security. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the concept of inter vlan routing configuration, its significance, benefits, and step-by-step implementation strategies. Whether you're an IT professional or a network enthusiast, this article will equip you with the knowledge to set up and optimize Inter-VLAN routing, ensuring a robust and efficient network infrastructure.
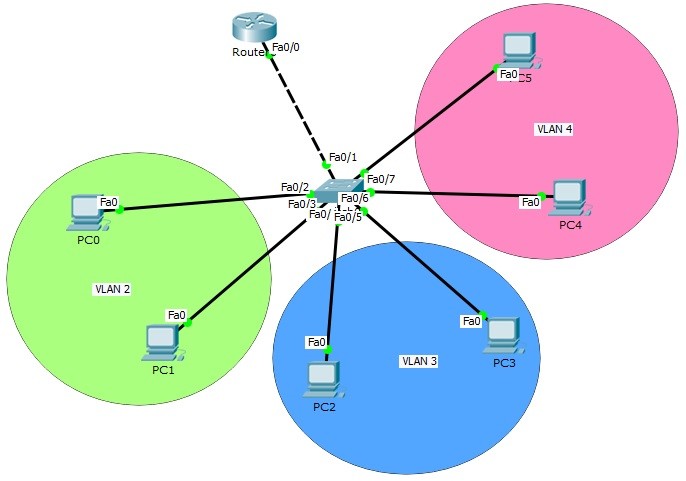
Section 1: Understanding Inter-VLAN Routing
Inter-VLAN routing is a networking technique that facilitates communication between different Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) within a single physical network. VLANs allow network administrators to logically segment a network into smaller, isolated broadcast domains, which enhances security and optimizes network performance.
However, without Inter-VLAN routing, these VLANs would remain isolated, hindering communication between devices residing in different VLANs. Inter-VLAN routing breaks down these barriers, enabling devices in different VLANs to exchange data and communicate seamlessly.
Inter-VLAN routing can be achieved through different methods, including:
- Router-on-a-stick: This method involves using a single physical router interface to route traffic between multiple VLANs.
- Layer 3 Switch: A Layer 3 switch is capable of routing traffic between VLANs, combining the functions of a switch and a router.
Section 2: The Benefits of Inter-VLAN Routing
Implementing Inter-VLAN routing offers various benefits to network administrators and end-users:
a. Enhanced Network Security: By isolating sensitive data and resources into separate VLANs, Inter-VLAN routing mitigates security risks and contains potential security breaches.
b. Improved Performance: Dividing the network into smaller broadcast domains reduces broadcast traffic and improves overall network performance.
c. Resource Optimization: Inter-VLAN routing allows efficient use of network resources by directing traffic to its intended destination, reducing unnecessary data flow.
d. Simplified Network Management: VLAN segmentation simplifies network management, making it easier to troubleshoot and implement changes.
Section 3: Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing
Follow these step-by-step guidelines to configure Inter-VLAN routing:
- Plan VLANs and IP Addressing: Determine the number of VLANs needed and allocate appropriate IP address ranges for each VLAN.
- Enable VLANs on Switch: Access the switch's management interface and create the necessary VLANs. Assign relevant ports to each VLAN.
- Configure VLAN Interfaces: For each VLAN, create a virtual interface on the router using the sub-interface command. Assign an IP address to each sub-interface.
- Enable Routing on the Router: Enable routing protocols, such as RIP (Routing Information Protocol) or OSPF (Open Shortest Path First), on the router to allow communication between VLANs.
- Set Default Gateway: Define a default gateway for devices within each VLAN to direct traffic between VLANs.
- Test Connectivity: Verify the Inter-VLAN routing configuration by testing communication between devices in different VLANs.
Section 4: Troubleshooting Inter-VLAN Routing
Despite careful configuration, issues may arise with Inter-VLAN routing. Here are some common troubleshooting tips:
a. Verify VLAN Configuration: Double-check VLAN configuration on switches and routers to ensure consistency.
b. Check IP Addressing: Verify that each VLAN interface has the correct IP address within the appropriate subnet.
c. Routing Protocol Configuration: Ensure that the routing protocols are correctly configured and enabled on the router.
d. Firewall Settings: Check firewall rules to ensure they are not blocking Inter-VLAN traffic.
Section 5: Security Considerations
While Inter-VLAN routing improves network efficiency, it also introduces security considerations:
a. Access Control Lists (ACLs): Implement ACLs to control traffic flow between VLANs and restrict unauthorized access.
b. VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP): Disable VTP on all non-trunking ports to prevent unauthorized VLAN propagation.
c. VLAN Hopping: Avoid using the default VLAN for sensitive data to prevent VLAN hopping attacks.
d. Regular Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify potential vulnerabilities and address them proactively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Inter-VLAN routing configuration is a crucial aspect of modern networking. By understanding its significance, benefits, and following proper implementation and security practices, network administrators can create a well-optimized and secure environment. Embrace Inter-VLAN routing to enhance network performance, security, and overall efficiency for your organization's network infrastructure.





Comments