Introduction
In the world of networking, implementing efficient virtual networks is essential to ensure seamless communication and data transfer between devices. Switched Virtual Interface (SVI) configuration in Packet Tracer offers a powerful solution for creating and managing virtual LANs, enabling network administrators to optimize network performance and security. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the concept of SVI, its significance, benefits, and step-by-step implementation using Packet Tracer, a popular network simulation tool. Whether you're an IT professional or a networking enthusiast, this article will equip you with the knowledge to build and maintain efficient virtual networks using svi packet tracer.
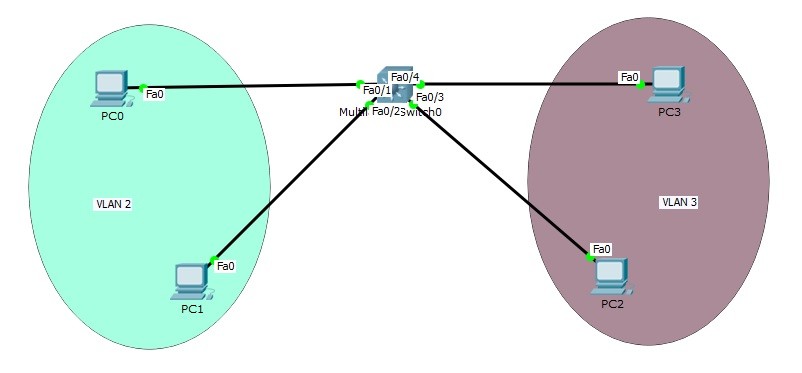
Section 1: Understanding SVI
Switched Virtual Interface (SVI) is a virtual interface on a Layer 3 switch, acting as a gateway for a specific VLAN. Unlike physical interfaces that connect to individual devices, SVIs are virtual, connecting to VLANs within the switch. These virtual interfaces allow communication between devices on the same VLAN and devices in other VLANs through Inter-VLAN routing.
SVI allows network administrators to configure routing protocols and access control lists (ACLs) on the switch, which enhances network segmentation, security, and performance. When a packet arrives at the switch destined for a device in the same VLAN, the switch forwards the packet directly within the VLAN. However, when the packet is destined for a device in a different VLAN, the SVI routes the packet to the appropriate VLAN, enabling Inter-VLAN communication.
Section 2: The Benefits of SVI Configuration
Implementing SVI configuration in Packet Tracer offers several key benefits:
a. Simplified Network Management: SVI allows administrators to manage multiple VLANs and routing configurations within a single device, simplifying network management.
b. Efficient VLAN Segmentation: SVI enables logical segmentation of the network into VLANs, preventing broadcast storms and optimizing network performance.
c. Inter-VLAN Communication: SVI facilitates communication between devices in different VLANs, enhancing connectivity and enabling centralized control.
d. Enhanced Network Security: By implementing ACLs on SVIs, administrators can control traffic flow between VLANs, enhancing network security.
Section 3: Configuring SVI in Packet Tracer
Follow these step-by-step guidelines to configure SVI in Packet Tracer:
- Create VLANs: Launch Packet Tracer and access the switch configuration mode. Create the required VLANs using the "vlan" command, assigning appropriate IDs and names.
- Enable VLANs on Ports: Assign specific ports to respective VLANs using the "interface range" command followed by "switchport access vlan [VLAN_ID]" for each interface.
- Configure SVI: Create the SVI for each VLAN using the "interface vlan [VLAN_ID]" command. Assign an IP address to the SVI using the "ip address [IP_ADDRESS] [SUBNET_MASK]" command.
- Enable Routing: Enable IP routing on the Layer 3 switch using the "ip routing" command, allowing Inter-VLAN communication.
- Test Connectivity: Use Packet Tracer's simulation mode to verify connectivity between devices in different VLANs, ensuring the SVI configuration works as expected.
Section 4: Troubleshooting SVI Configuration
Despite careful configuration, issues may arise with SVI in Packet Tracer. Here are some common troubleshooting tips:
a. VLAN Membership: Check that ports are correctly assigned to the appropriate VLANs.
b. IP Addressing: Verify that each SVI has the correct IP address within the correct subnet.
c. Routing Configuration: Ensure that IP routing is enabled on the Layer 3 switch.
d. Connectivity Testing: Use Packet Tracer's built-in tools to test connectivity and pinpoint potential issues.
Section 5: Real-World Applications of SVI Configuration
SVI configuration in Packet Tracer finds applications in various real-world scenarios:
a. Enterprise Networks: In large organizations, SVI simplifies network management and enhances scalability by enabling effective VLAN segmentation and Inter-VLAN communication.
b. Data Centers: Data centers benefit from SVI configuration as it streamlines network management, optimizes performance, and enhances security across multiple VLANs.
c. Campus Networks: Educational institutions and campus networks benefit from SVI as it allows seamless communication between different departments and user groups while maintaining data separation.
d. Network Labs: SVI in Packet Tracer is widely used for educational purposes in network labs, providing a safe and realistic environment to practice network configuration and troubleshooting.
Conclusion
In conclusion, SVI configuration in Packet Tracer offers a powerful solution for creating efficient virtual networks. By understanding its significance, benefits, and following the step-by-step implementation guide, network administrators can leverage SVI to optimize performance, enhance security, and enable seamless communication within their networks. Embrace SVI to build robust and scalable virtual networks for your organization's networking needs.





Comments