Introduction
The Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) is a dynamic routing protocol developed by Cisco, designed to efficiently manage and exchange routing information within a network. Cisco Packet Tracer, a powerful network simulation tool, provides an excellent platform to understand and practice EIGRP configurations in a safe and controlled environment. In this comprehensive blog post, we will explore the significance of EIGRP in modern networking, learn how to configure eigrp cisco packet tracer, and discover the benefits of this protocol for dynamic and scalable routing in enterprise networks.
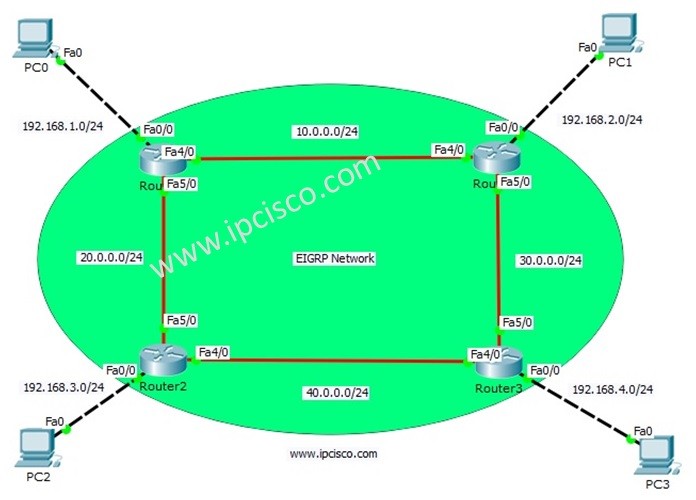
Section 1: Understanding EIGRP
EIGRP is an advanced distance-vector routing protocol that supports fast convergence, low bandwidth consumption, and load balancing across multiple paths. It is classified as a hybrid routing protocol because it combines the features of both distance-vector and link-state protocols. EIGRP uses the Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL) to ensure loop-free routing and to quickly adapt to network topology changes.
Section 2: Configuring EIGRP on Cisco Routers in Packet Tracer
Step 1: Enable EIGRP on the Router In Packet Tracer, access the router's CLI and enable EIGRP globally using the "router eigrp [AS-number]" command. The AS-number is the autonomous system number, which is used to identify the EIGRP domain.
Step 2: Configure Networks to Participate in EIGRP Identify the networks that should participate in EIGRP by using the "network [network-address]" command. This command specifies which interfaces and IP subnets should be advertised via EIGRP.
Step 3: Adjust Metric Weights (Optional) By default, EIGRP calculates its metric based on bandwidth and delay. However, you can fine-tune metric calculations using the "metric weights" command to give more weight to specific factors like delay or reliability.
Step 4: Verify EIGRP Configuration Use the "show ip eigrp interfaces" and "show ip eigrp neighbors" commands to verify EIGRP configuration and adjacency status.
Section 3: Benefits of EIGRP in Enterprise Networking
- Fast Convergence: EIGRP's rapid convergence time ensures that the network quickly adapts to topology changes, minimizing downtime and ensuring optimal path selection.
- Efficient Bandwidth Utilization: EIGRP uses partial updates, sending only the necessary routing information when network changes occur, reducing the amount of bandwidth consumed.
- Load Balancing: EIGRP supports unequal-cost load balancing, enabling traffic distribution across multiple paths based on their respective metrics.
- Backward Compatibility: EIGRP is backward compatible with classic distance-vector protocols, allowing for easy migration and coexistence with older routing protocols.
Section 4: Practical Implementation of EIGRP in Packet Tracer
Using Packet Tracer, simulate a network scenario with multiple routers and switches. Configure EIGRP on the routers and observe how they form adjacencies and exchange routing information. Implement network changes to see how EIGRP rapidly adapts and updates the routing tables, ensuring optimal path selection.
Section 5: Troubleshooting EIGRP in Packet Tracer
Common issues when configuring EIGRP in Packet Tracer include misconfigured network statements or access control lists (ACLs) blocking routing updates. Troubleshoot these issues by verifying EIGRP configuration on all routers and ensuring that the appropriate network interfaces are included in the EIGRP process.
Section 6: Conclusion
EIGRP is a powerful and efficient routing protocol designed to enhance network performance and scalability. In Cisco Packet Tracer, network enthusiasts, students, and professionals can practice EIGRP configuration to gain valuable hands-on experience with this dynamic routing protocol. By implementing EIGRP in enterprise networks, administrators can achieve fast convergence, efficient bandwidth utilization, and optimal load balancing, ensuring a stable and resilient network infrastructure. Embrace EIGRP in Packet Tracer to elevate your routing skills and stay ahead in the ever-evolving world of networking.





Comments