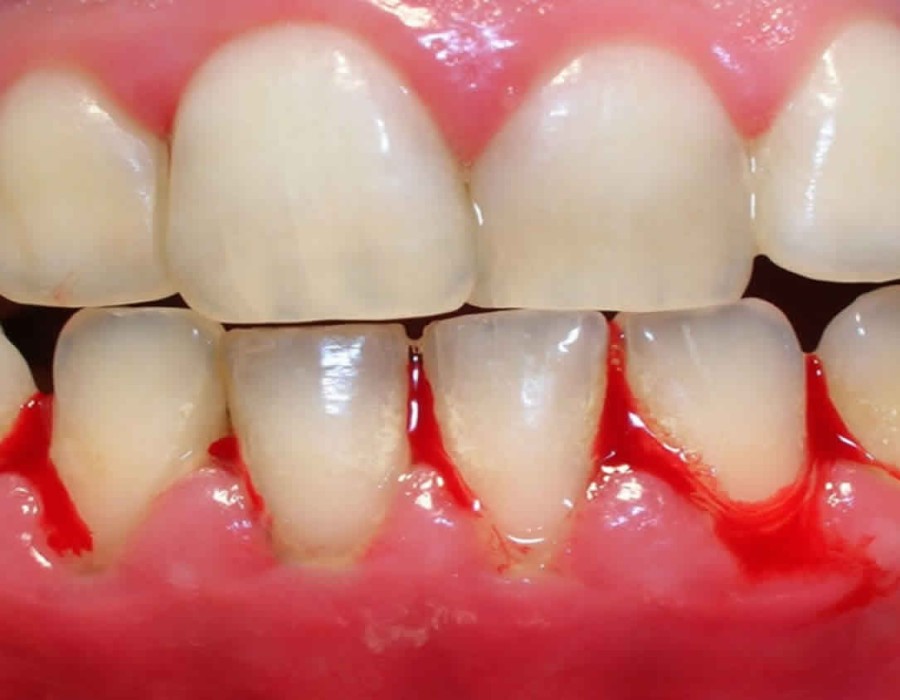
Gum bleeding, also known as gingival bleeding, can be a concerning issue for many individuals. While factors like poor oral hygiene and gum disease are commonly associated with this condition, the role of genetics in gum bleeding is often overlooked. In this article, we delve into Gum Bleeding in Dubai the fascinating connection between genetics and gum bleeding, exploring how our genes can influence the health of our gums.
What Causes Gum Bleeding?
Before delving into the genetic aspects, it's essential to understand the common causes of gum bleeding. Poor oral hygiene, which leads to the buildup of plaque and tartar, is a primary culprit. Gingivitis, the early stage of gum disease, can also cause bleeding gums. Other factors such as hormonal changes, certain medications, and systemic diseases like diabetes can contribute to gum bleeding as well.
The Genetic Influence
While environmental factors play a significant role in gum health, genetics also play a crucial part. Research has shown that some individuals may be predisposed to gum disease and related symptoms like gum bleeding due to their genetic makeup. Certain genetic variations can affect how the immune system responds to bacteria in the mouth, increasing the likelihood of developing gum problems.
Genetic Markers and Risk Assessment
Scientists have identified specific genetic markers associated with an increased risk of gum disease and gum bleeding. These markers can be inherited from parents and contribute to variations in how individuals respond to oral bacteria and inflammation. Understanding these genetic factors can help in assessing an individual's susceptibility to gum bleeding and implementing preventive measures.
The Role of Inflammation
Inflammation plays a crucial role in the development and progression of gum disease. Genetic variations can influence how the immune system regulates inflammation in the gums. Some individuals may have an exaggerated inflammatory response to bacterial toxins, leading to more severe gum inflammation and bleeding. By identifying these genetic predispositions, healthcare professionals can tailor Gum treatment approaches to manage inflammation effectively.
Genetic Testing for Gum Health
Advancements in genetic testing have made it possible to assess an individual's genetic predisposition to gum disease. By analyzing specific genetic markers, healthcare providers can identify patients who may be at a higher risk of developing gum bleeding and other oral health issues. This information allows for personalized preventive strategies and early intervention to maintain gum health.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
While genetics play a significant role, lifestyle and environmental factors also influence gum health. Maintaining good oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing and flossing, can help prevent plaque buildup and reduce the risk of gum bleeding. Additionally, avoiding tobacco use and consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables can support gum health.
The Interplay Between Genetics and Environment
It's essential to recognize that genetics and environmental factors interact in complex ways to determine an individual's susceptibility to gum bleeding. While genetics may predispose someone to Gum Bleeding disease, lifestyle choices and environmental exposures can either exacerbate or mitigate these genetic risks. Understanding this interplay is crucial for developing effective preventive strategies.
Conclusion
Gum bleeding is not solely caused by poor oral hygiene or gum disease; genetics also play a significant role in determining an individual's susceptibility to this condition. By understanding the genetic factors involved, healthcare professionals can better assess patients' risk of developing gum bleeding and tailor preventive measures accordingly. Through a combination of genetic testing, lifestyle modifications, and personalized care, it's possible to maintain optimal gum health and prevent issues like gum bleeding in susceptible individuals.




Comments