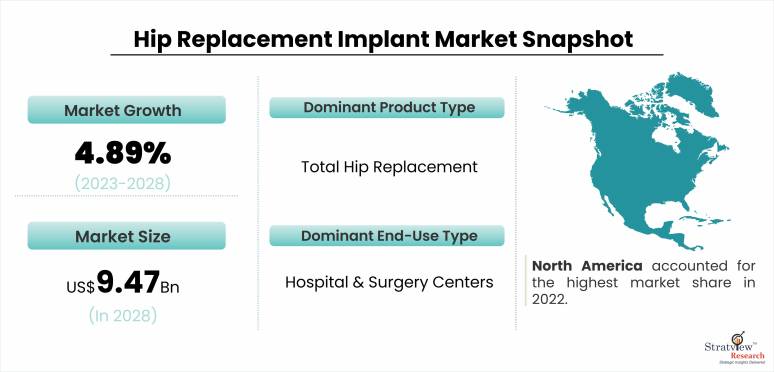
Hip replacement surgery has long been recognized as a highly effective solution for individuals suffering from severe hip joint pain and disability. Over the years, remarkable advancements in technology have transformed the field of orthopedics, particularly in the development of hip replacement implants. These advancements have revolutionized patient outcomes, improving the durability, functionality, and overall success of hip replacement procedures. The hip replacement implant market is estimated to grow from USD 7.09 billion in 2022 to USD 9.47 billion by 2028 at a healthy CAGR of 4.89% during the forecast period.
Traditionally, hip replacement implants consisted of metal-on-polyethylene components. While these implants provided relief for many patients, they had limitations in terms of longevity and wear resistance. However, recent technological breakthroughs have addressed these issues, leading to the introduction of innovative materials and designs that have significantly enhanced the performance and lifespan of hip implants.
One major advancement is the utilization of highly durable and biocompatible materials, such as ceramic and metal alloys. Ceramic implants, made of materials like zirconia or alumina, offer exceptional strength and wear resistance, minimizing the risk of implant fracture and reducing the need for revision surgeries. Metal alloys, including titanium and cobalt-chromium, provide excellent corrosion resistance, biomechanical stability, and longevity. These materials have transformed the landscape of hip replacement surgery, enabling implants to withstand the demands of daily activities for longer periods.
In addition to improved materials, advancements in implant design have played a crucial role in enhancing patient outcomes. One notable innovation is the development of modular hip implants. These implants consist of separate components, such as stems, heads, and cups, which can be individually tailored to the patient's specific anatomy. This modularity allows for better alignment, stability, and range of motion, leading to improved functionality and patient satisfaction. Furthermore, modular implants facilitate easier revision surgeries if required, minimizing tissue disruption and improving outcomes for patients who may need future interventions.
Another significant advancement is the advent of minimally invasive techniques in hip replacement surgery. Traditional hip replacement procedures involve large incisions and extensive tissue disruption, resulting in longer recovery times and increased risk of complications. However, with the introduction of minimally invasive approaches, such as anterior and posterior-lateral approaches, surgeons can now perform hip replacements through smaller incisions, sparing muscles and tendons. This approach reduces postoperative pain, shortens hospital stays, and accelerates rehabilitation, enabling patients to regain their mobility and independence faster.
Technological advancements have also revolutionized the use of robotics and computer-assisted navigation systems in hip replacement surgery. Robotic systems offer precise preoperative planning, intraoperative guidance, and real-time feedback to the surgeon, resulting in more accurate implant placement and alignment. This level of precision reduces the risk of complications, improves implant longevity, and enhances patient satisfaction. Computer-assisted navigation systems provide similar benefits, aiding surgeons in achieving optimal positioning and alignment of the implants.
Furthermore, the integration of digital technologies has facilitated personalized patient care and improved postoperative monitoring. Wearable devices and mobile applications allow patients to track their recovery progress, monitor physical activity levels, and receive personalized exercise regimens. These digital tools not only promote patient engagement but also enable healthcare providers to gather valuable data for assessing outcomes, identifying potential issues, and optimizing postoperative care.
In conclusion, technological advancements in hip replacement implants have transformed the field of orthopedics and revolutionized patient outcomes. The utilization of advanced materials, such as ceramics and metal alloys, along with modular designs, has significantly enhanced implant durability and functionality. Minimally invasive techniques, robotic assistance, and computer-assisted navigation systems have improved surgical precision and patient recovery. The integration of digital technologies has further personalized patient care and facilitated postoperative monitoring. With ongoing research and development, the future holds even more promising advancements, ensuring that hip replacement surgery continues to provide lasting relief and improved quality of life for patients worldwide.




Comments